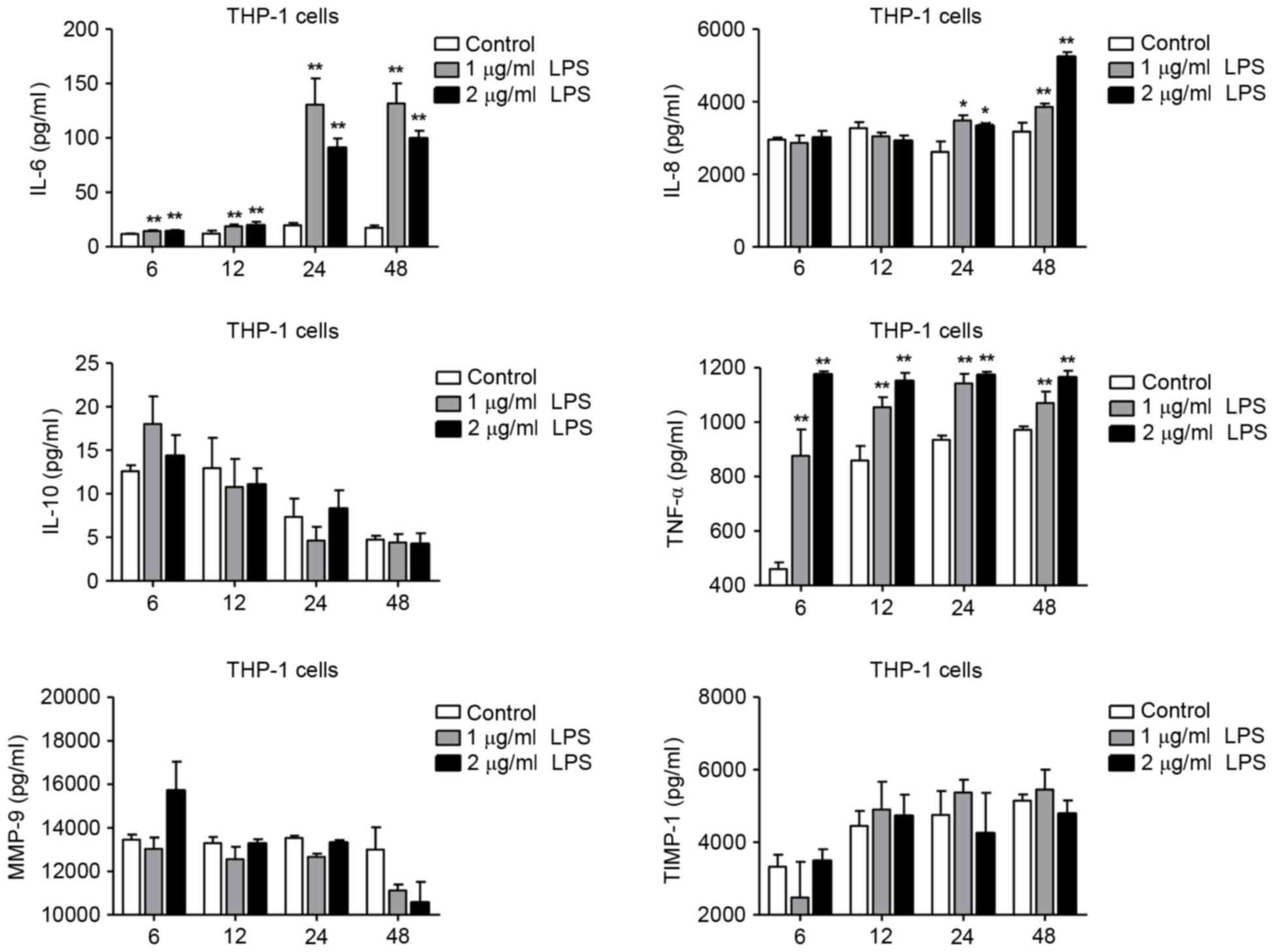
LPS‑induced proinflammatory cytokine expression in human airway epithelial cells and macrophages via NF‑κB, STAT3 or AP‑1 activation

Lipopolysaccharide-mediated IL-10 transcriptional regulation requires sequential induction of type I IFNs and IL-27 in macrophages. - Abstract - Europe PMC

Suppressive Effect on Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Proinflammatory Mediators by Citrus aurantium L. in Macrophage RAW 264.7 Cells via NF- B Signal Pathway

Metformin Suppresses Lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced Inflammatory Response in Murine Macrophages via Activating Transcription Factor-3 (ATF-3) Induction* - Journal of Biological Chemistry

SciELO - Brasil - Selenium protects against LPS-induced MC3T3-E1 cells apoptosis through modulation of microRNA-155 and PI3K/Akt signaling pathways Selenium protects against LPS-induced MC3T3-E1 cells apoptosis through modulation of microRNA-155 and ...

Lipopolysaccharide-Related Stimuli Induce Expression of the Secretory Leukocyte Protease Inhibitor, a Macrophage-Derived Lipopolysaccharide Inhibitor | Infection and Immunity

A Novel Class of Antioxidants Inhibit LPS Induction of Tissue Factor by Selective Inhibition of the Activation of ASK1 and MAP Kinases | Arteriosclerosis, Thrombosis, and Vascular Biology

Xanthohumol ameliorates lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced acute lung injury via induction of AMPK/GSK3β-Nrf2 signal axis - ScienceDirect
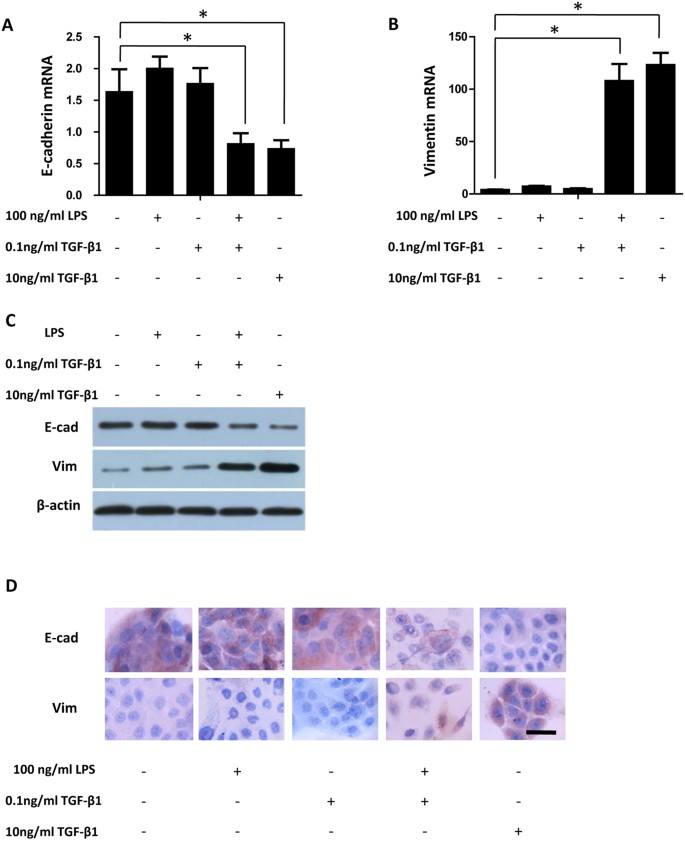
LPS/TLR4 Signaling Enhances TGF-β Response Through Downregulating BAMBI During Prostatic Hyperplasia | Scientific Reports

Lipopolysaccharide-induced Expression of Interferon-β Mediates the Timing of Inducible Nitric-oxide Synthase Induction in RAW 264.7 Macrophages* - Journal of Biological Chemistry

LPS Induces Occludin Dysregulation in Cerebral Microvascular Endothelial Cells via MAPK Signaling and Augmenting MMP-2 Levels

Lipopolysaccharide activation of the MEK-ERK1/2 pathway in human monocytic cells mediates tissue factor and tumor necrosis factor α expression by inducing Elk-1 phosphorylation and Egr-1 expression: Presented in abstract form at the

Dexamethasone enhances LPS induction of tissue factor expression in human monocytic cells by increasing tissue factor mRNA stability - Reddy - 2004 - Journal of Leukocyte Biology - Wiley Online Library

A Novel Class of Antioxidants Inhibit LPS Induction of Tissue Factor by Selective Inhibition of the Activation of ASK1 and MAP Kinases | Arteriosclerosis, Thrombosis, and Vascular Biology
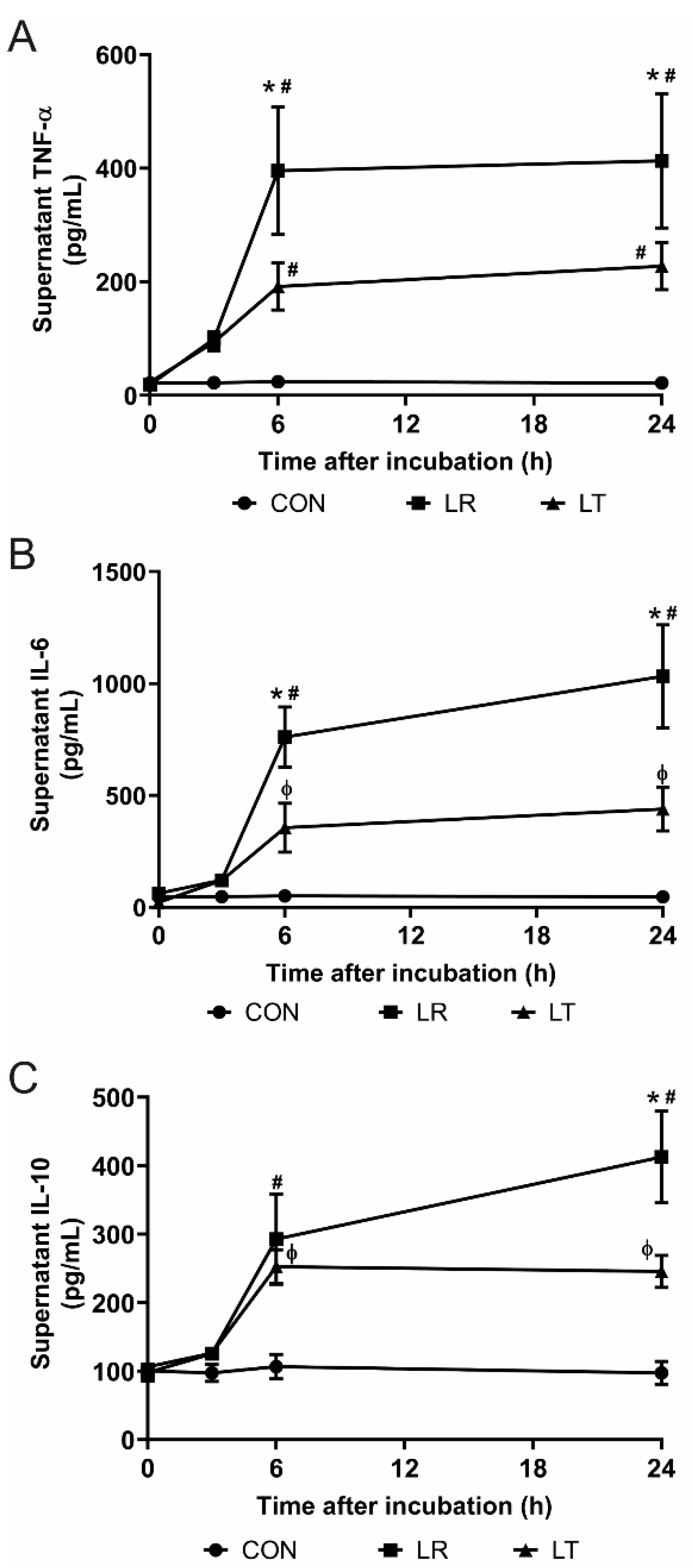
Biomolecules | Free Full-Text | LPS Tolerance Inhibits Cellular Respiration and Induces Global Changes in the Macrophage Secretome | HTML

Lipopolysaccharide-Mediated IL-10 Transcriptional Regulation Requires Sequential Induction of Type I IFNs and IL-27 in Macrophages | The Journal of Immunology
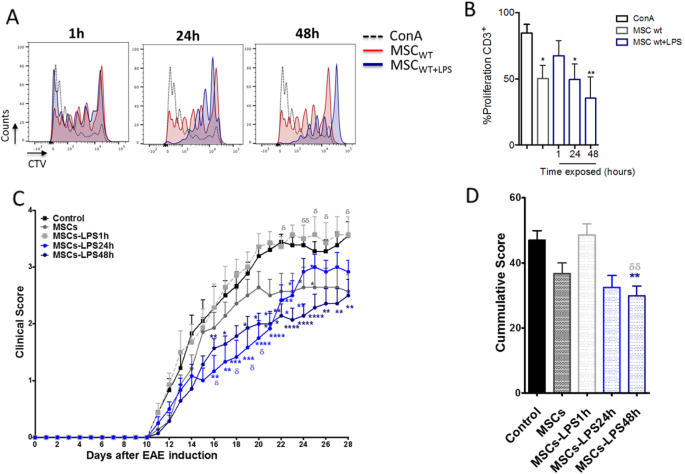
Time-dependent LPS exposure commands MSC immunoplasticity through TLR4 activation leading to opposite therapeutic outcome in EAE | Stem Cell Research & Therapy | Full Text
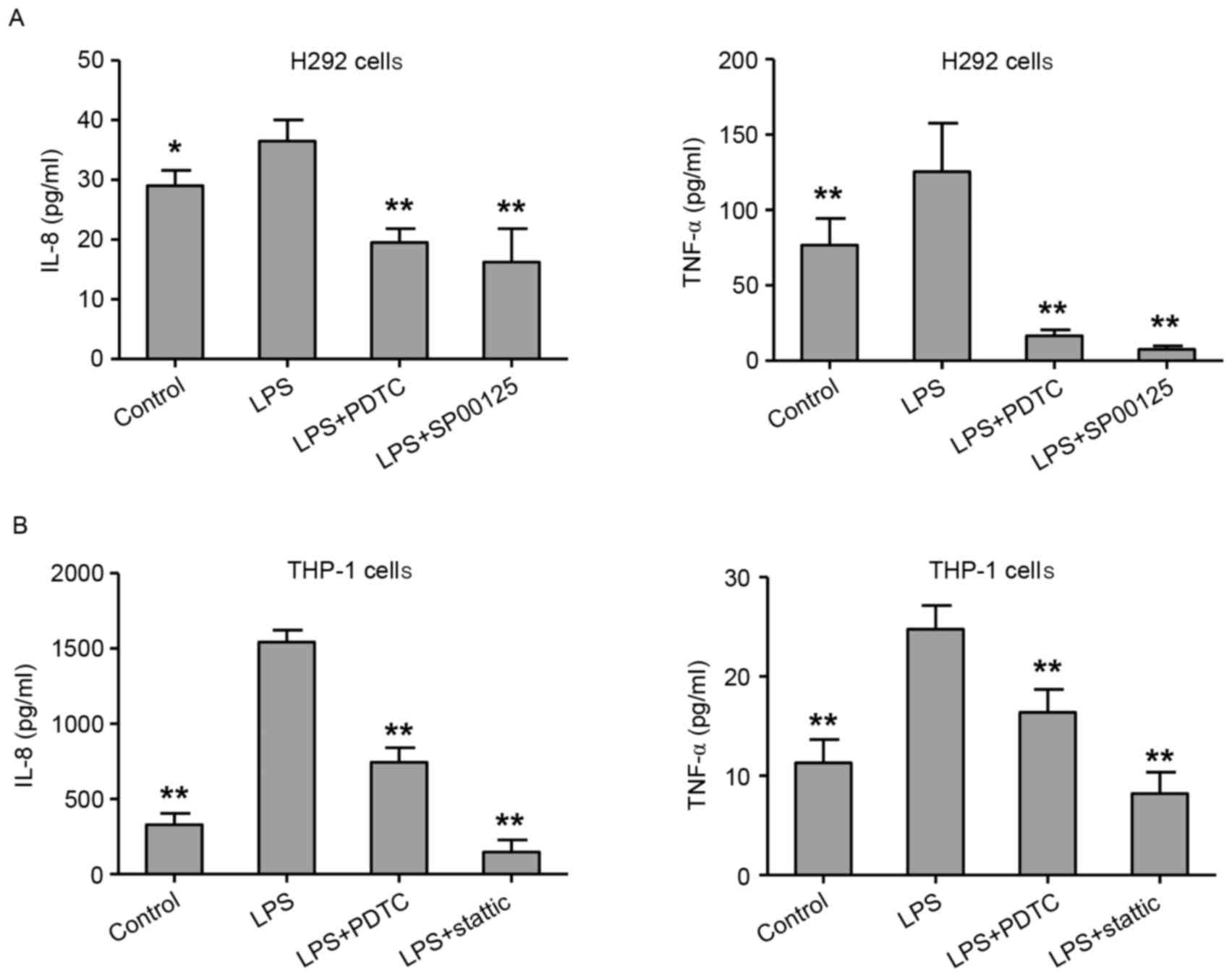
LPS‑induced proinflammatory cytokine expression in human airway epithelial cells and macrophages via NF‑κB, STAT3 or AP‑1 activation
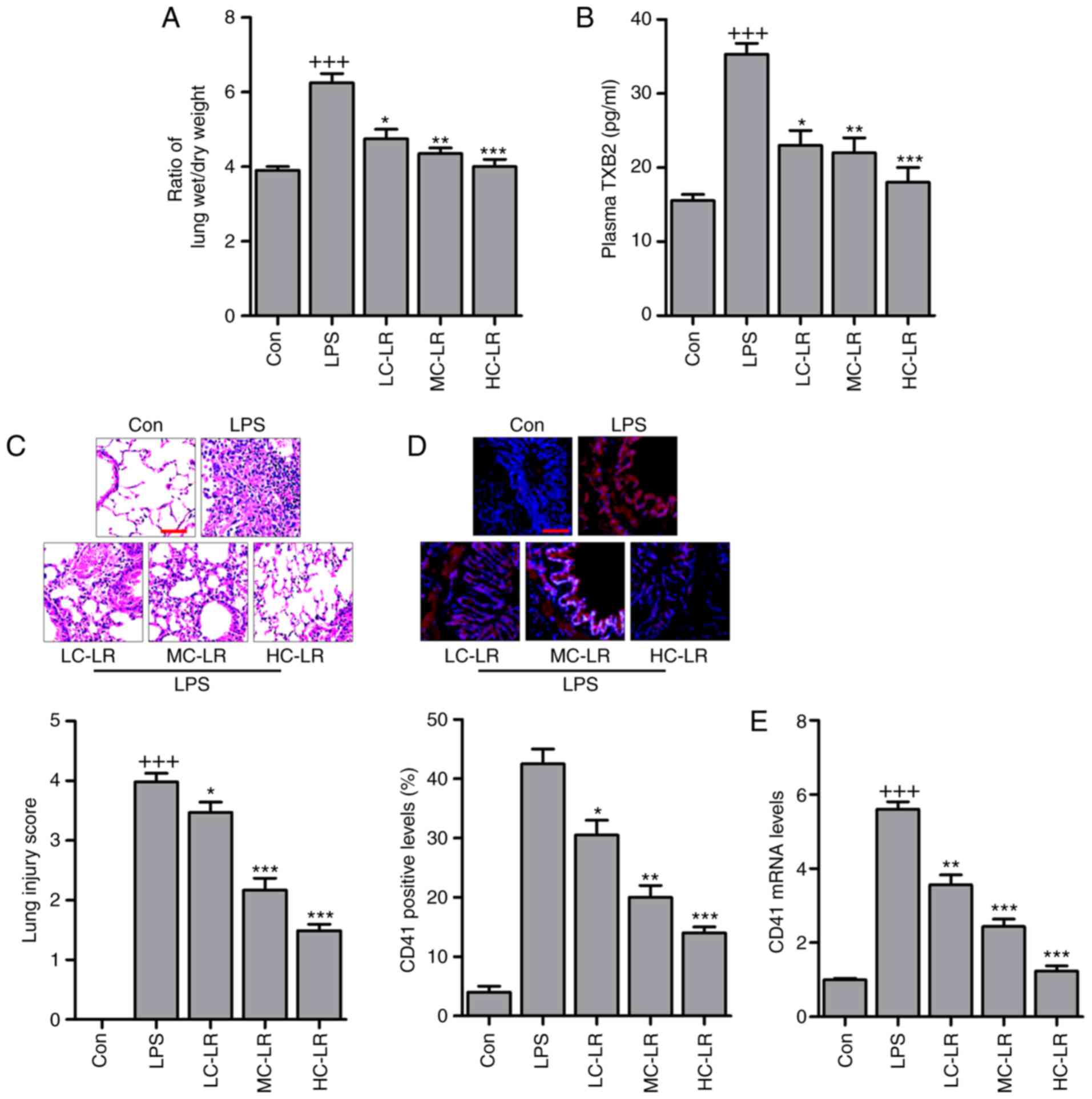
Linarin prevents LPS‑induced acute lung injury by suppressing oxidative stress and inflammation via inhibition of TXNIP/NLRP3 and NF‑κB pathways
PLOS ONE: 2-phenylethynesulfonamide Prevents Induction of Pro-inflammatory Factors and Attenuates LPS-induced Liver Injury by Targeting NHE1-Hsp70 Complex in Mice

LPS platelet stimulation requires IL-1b production. (A) LPS induction... | Download Scientific Diagram

Lipopolysaccharides induced inflammatory responses and electrophysiological dysfunctions in human-induced pluripotent stem cell derived cardiomyocytes | Scientific Reports



